

MARK WATSON | CONTENT HEAD
22
Feb, 2024Struggling with a weak car battery can throw a wrench into any driver's day. Car batteries, essential for starting your vehicle and powering onboard electronics, sometimes give out unexpectedly.
If you want to change a car battery, you are on the right page. Let's explore the key findings from this article.
Key Takeaways
Car batteries come in several types, such as lead-acid, AGM, deep cycle, Li-ion, and EFB, each designed to meet the energy demands of different vehicles.
Signs that a car battery needs replacing include slow engine cranking, dimming lights, electrical issues, swollen casing or corrosion on the battery terminals.
To replace a car battery safely, turn off the engine, disconnect the negative than positive battery terminals, remove clamps or attachments, and lift out the old battery before cleaning and installing a new one.
Proper disposal of an old car battery is essential - take it to a recycling centre or auto parts store to avoid environmental harm.
Reconnecting your new battery involves attaching positive and negative cables securely; recharging can be done with various chargers or through jump-starting if necessary.
Understanding Car Batteries
Want to change a car battery? It's crucial to not only recognize when a battery is nearing the end of its life but also to understand the variety available and how they differ, Doing this will make sure you're equipped with knowledge for smooth operation or timely replacement.
The function of a car battery
A car battery serves as the heart of your vehicle's electrical system. It delivers the necessary power to start the engine and provides energy for all the electrical components when the engine is off.
Picture turning your key in the ignition; it’s the battery that sends a surge of electricity to get things moving. This 12-volt lead-acid powerhouse runs everything from headlights to your car's computer system.
Car batteries also stabilise voltage to keep your engine running smoothly. Without this consistent source of power, modern vehicles wouldn't be able to function—the alternator alone isn’t enough during startup.
Batteries store excess energy too, ensuring there’s always a reserve whenever you need that extra jolt for systems like high-powered stereos or navigation screens in hybrid and electric cars with much longer-lasting batteries driving their complex electronics.
Types of car batteries
Car batteries come in different varieties, each suited for specific vehicle types and needs. Choosing the right type can ensure better performance and longevity for your automobile.
Lead-Acid Batteries: These are the most common type of car batteries and are used in a wide range of vehicles. They're affordable, reliable, and typically have a 12-volt output suitable for most standard cars. Despite their popularity, they require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries: AGM batteries cater to vehicles with higher energy demands. They’re excellent for stop-start systems and support features that require a constant power supply, like heated seats or high-end audio systems. Durability is a key advantage here as they can withstand intense vibrations.
Deep Cycle Batteries: Unlike standard car batteries, deep cycle variants provide steady power over longer periods. They excel in electric or hybrid vehicles due to their ability to be discharged and recharged repeatedly without losing capacity.
Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries: Often found in pure-electric cars, Li-ion batteries boast an extended lifespan which can reach up to 10 years or 100,000 miles. While more expensive upfront, these lightweight batteries offer high energy density and rapid recharging capabilities compared to traditional lead-acid options.
EFB (Enhanced Flooded Battery): EFB technology is an improvement on conventional lead-acid designs. These are particularly suited for micro-hybrid vehicles with start-stop functions, providing increased cycle life and improved charge acceptance.
Signs of car battery issues
Transitioning from the various types available, it's crucial to recognise when your car battery fails or start showing such signs. Most car batteries will show engine cranking is a classic red flag indicating that your battery might be on its last legs.
If you turn the key and the engine turns over more sluggishly than usual, it’s time to check your battery's state of charge and potentially change a car battery.
Noticeable dimming of headlights or interior lights also points towards a weak battery struggling to meet power demands. Electrical issues such as flickering dash lights or accessories that don't operate correctly can signal deeper problems with the battery connections or its ability to hold a charge.
A swollen battery casing implies potential damage from excessive heat, while visible corrosion on the battery terminals suggests electrical resistance which could hinder performance. Regularly inspecting these elements will help catch any early signs before they escalate into larger issues requiring urgent attention and possibly leaving you stranded.
Replacing a Car Battery
Need to change a car battery? Don't worry – it does not need to be a daunting task. With the right tools and know-how, it's a straightforward procedure you can accomplish at home. Unleash your inner mechanic as we guide you through the critical steps to safely remove your old battery and ensure you're equipped with the perfect replacement.
Step-by-step guide to safely remove the old battery
Removing an old car battery is straightforward if you follow the right steps. Before starting, ensure your vehicle’s engine is off and you’re wearing protective gloves and eyewear.
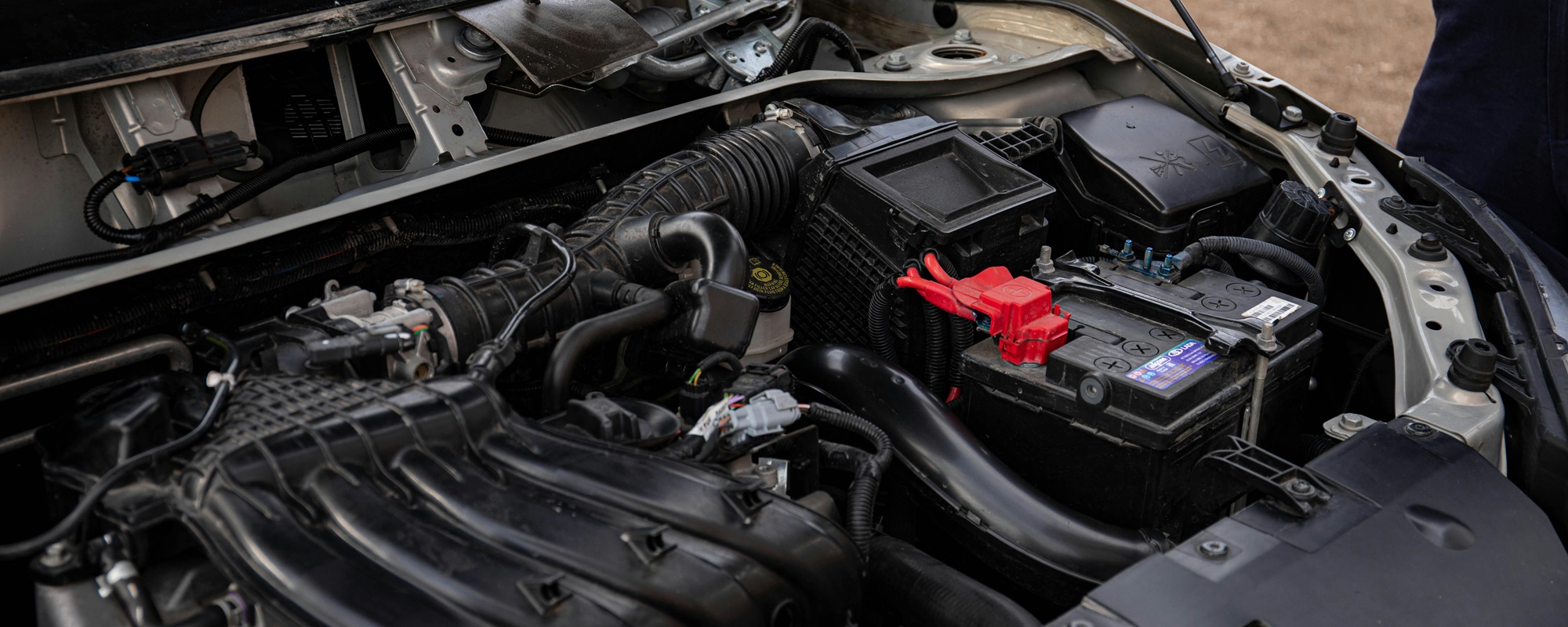
Locate the battery under the hood, which typically sits on either side of the engine bay.
Start by disconnecting the negative ( - ) terminal using a socket wrench or spanner to loosen the nut.
Carefully remove the cable from the negative terminal to avoid any sparks.
Proceed to disconnect the positive (+) terminal in the same manner, loosening its nut with a wrench and removing the cable.
Unfasten any clamps or retaining systems holding the battery in place using appropriate tools, often a ratchet or spanner will be needed here.
Check for any other attachments such as cable ties or electrical connections that may also need removing.
Gently lift the old battery out of its seat; batteries can be heavy, so keep a firm grip and use proper lifting techniques to avoid injury.
Clean off any corrosion from cable connectors and around where the battery sits – this helps prepare for installing a new battery.
Choosing the right replacement battery
Selecting an appropriate car battery replacement for your car is crucial; it influences performance and longevity. Check the owner's manual or look on the existing battery for specifications such as size, type, and voltage—larger vehicles typically require batteries with higher voltage to satisfy their power needs.
Always ensure the new battery matches these specs precisely.
Consider how long you intend to keep your vehicle when deciding on a battery grade. If you're planning several more years of use, investing in a high-quality brand like Pirelli or Michelin can save future headaches.
Remember that while electric cars have different requirements and their batteries last longer—often upwards of 10 years—the initial car battery cost can be higher, starting from around £200 without including car battery fitting charges by a professional mechanic.
Make sure compatibility with your engine type is clear; diesel engines may demand more sturdy options than those designed for petrol combustion systems.
Proper disposal of the old battery
Once you've successfully replaced your car battery, the next crucial step is to dispose of the old one responsibly. Don’t just chuck it in the bin or leave it lying around; lead-acid batteries contain harmful materials that can wreak havoc on the environment.
Instead, take your used automotive battery to a certified recycling centre or return it to a local auto parts store. These places work with your vehicle's electrical systems to handle car battery recycling, ensuring all components are properly sorted and processed.
Recycling centres break down old batteries to reclaim valuable materials like lead, plastic, and acid which can be reused for new products. This process significantly reduces the need for fresh resources and minimises environmental damage by keeping toxic substances out of landfills and water sources.
By choosing responsible disposal methods for your old battery, you're contributing positively not just to environmental protection but also supporting resource recovery efforts within your community.
Reconnecting and Recharging
Once your new battery is in place in the battery tray, mastering the reconnection process will ensure a smooth start-up and knowing how to recharge it properly will keep you on the road without hitches – continue reading for our expert tips.
Reconnecting the new battery
Installing a new car battery is straightforward if you follow the correct steps. Ensure your vehicle is off and the keys are out of the ignition before starting.
Park your car on a flat surface, engage the parking brake and pop open the hood.
Wear some protective gloves; batteries contain acidic materials that can harm your skin.
Find the new battery and carefully place it in the battery tray, positioning it to match the old one's orientation.
Connect the positive battery terminal first; this is usually marked with a plus (+) sign or covered by a red cap.
Securely fasten the positive cable onto the positive terminal to ensure a good connection.
Move on to the negative battery terminal, typically indicated by a minus ( - ) sign or with a black cover.
Attach and tighten down your negative cable onto its corresponding negative terminal.
Double-check both connections are tight because loose cables can cause problems when starting your car.
Dispose of your old lead-acid battery responsibly by taking it to an automotive shop or scrapyard; they have proper recycling systems in place.
Recharging options and time
Once you've got your new car battery connected, it's time to focus on recharging. You have a couple of options for this: using a standard car battery charger, picking between a speed charger and a trickle charger depending on how fast you need the job done.
Speed chargers will do the work quickly but must be monitored to prevent overcharging while trickle chargers take longer but can be left connected for extended periods without risk.
Jump-starting is another route if your battery needs an immediate boost. It requires jumper cables and another vehicle that's already running or a portable jump starter. Remember, charging times vary based on the method used and the current state of your battery.
Typically, expect anywhere between two to eight hours to fully recharge using a charger. However, in some scenarios where batteries are deeply discharged, it might take up to 24 hours before they're back up at full capacity.
Keep an eye on progress by checking with a multimeter; when it reads around 12.6 volts or above - that signals your battery is charged and ready!
Conclusion
Changing a car battery at home isn't as daunting as it sounds. With the right tools and a bit of knowledge, you can get your vehicle up and running in no time. Remember to always put safety first and follow each step carefully to avoid any mishaps.
Keep this guide handy for when it's time to give your car that fresh spark of energy! It's an empowering skill that saves both time and money, ensuring you're never left stranded with a dead battery.
FAQs
1. Can I change my car battery at home?
Absolutely, you can replace a car battery yourself with the right tools and safety precautions; ensuring your vehicle maintains its power for a smooth start every time.
2. What steps should I follow to safely replace a car battery?
Start by turning off your engine and removing the keys. Use gloves and eye protection, disconnect the negative cable first, followed by the positive one, then lift out the old battery and place in the new one securely.
3. Is bump starting a manual transmission car okay if my battery dies?
Yes, bump starting or push starting is possible on manual transmission cars when facing a dead battery situation – it’s done by pushing or rolling down an incline to jump-start the engine.
4. How do weather conditions like humidity affect automotive batteries?
Extreme cold or heat can indeed impact lead acid batteries significantly—causing them to work harder which might reduce their lifespan compared to normal humidity levels.
5. When should I consider getting my tyre code checked during maintenance routines such as changing batteries?
Examining your tyres' sidewall codes is wise during routine checks; this will ensure optimal compatibility with your Elantra or any vehicle type you own because these codes disclose crucial information about tyre width and other specifications.

















































































No comments